|
Ampicillin
+ Cloxacillin
|
Penicillins & Cephalosporins possess a ß-lactam
ring in their nucleus, hence known as ß-lactam antibiotics.
Simplified structure
of nucleus
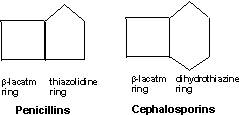
|
Many bacteria
are capable of producing ß-lactamase, an enzyme which breaks
the ß-lactam ring, rendering the antibiotic ineffective
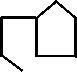
Simplified
diagram to show break in ß-lactam ring
|
ß-lactamase
producing bacteria are widely prevalent and include
- Staphyloccus aureus (especially notorious)�
- Haemophilus influenzae�
- Escherichia coli�
- Proteus spp.�
- Salmonella spp.�
- Bacteroides�
- Neisseria spp.
- And others
Hence
ß-lactamase induced resistance is an important problem
|
|
Ampicillin
-
a penicillin - one of the greatest drugs ever, with time tested efficacy
and safety
- broad spectrum coverage of bacteria causing day-to-day infections
Butů...
inactivated by ß-lactamase
|
The
Need...
- An antibiotic
which covers both
ß-lactamase- producing and
non-ß-lactamase-producing bacteria
- With
time tested efficacy and safety of penicillins
|
Ampicillin
+ Cloxacillin�meets the need!
- 2 time-tested
penicillins known for their efficacy and safety
-ß-lactamase stability of cloxacillin makes it an appropriate
companion to ampicillin
- coverage against both ß-lactamase-producing and
non-ß-lactamase-producing bacteria
|
Ampicillin
+ Cloxacillin
Broad spectrum
combination for day-to-day infections, particularly situations where
Staph. aureus may be involved, and in mixed infections
|
Ampicillin
- Aminopenicillin,
possesses broad spectrum coverage against gram +ve and gram -ve bacteria
- Acts
by inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis
- Bactericidal
effect
- Covers
streptococci, H.influenzae, E. coli, Salmonella, Shigella, Proteus
mirabilis, Neisseria
- Inactivated
by bacterial ß-lactamase
|
Cloxacillin
- Isoxazolyl
penicillin, possesses narrow spectrum coverage chiefly against gram
+ve bacteria, especially staphylococci (drug of choice against Staph.
aureus)
- Stable
against many bacterial ß-lactamases
- Acts
by inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis
- Bactericidal
effect
- Covers
staphylococci (inhibits ß-lactamase and also bactericidal against
staphylococci), some streptococci and Neisseria
|
Ampicillin
+ cloxacillin suited for combination because
- They
act synergistically in combination
- Similar
pharmacokinetic profile (both administered 6 hourly)
- Chemically
compatible for combination - No drug interactions
|
Comparative features
| |
Ampicillin
|
Cloxacillin
|
|
Administration
|
Oral,
IM, IV
|
Oral,
IM, IV
|
|
Oral
absorption
|
Good
|
Good
|
|
Peak
levels
|
1-2
hrs
|
1-2
hrs
|
|
Tissue
distribution
|
Good
|
Good
|
|
Half
life
|
1/2-1
hrs
|
1/2-1
hrs
|
|
Fate
|
Mostly
excreted unchanged in urine & stools
|
Minimal
metabolism in liver; excreted unchanged in urine |
|
Frequency
of adm
|
6
hrly
|
6
hrly
|
|
|
Benefits
of combination
Synergism
* antibacterial effect against organisms not covered by either drug
alone (lower MIC makes same tissue concentration more effective)�
* wider spectrum�
* efficacy in lower doses�
* greater efficacy
ß-lactamase
inhibition
*
Cloxacillin is resistant to staphylococcal beta-lactamase and also
inhibits ß-lactamases produced by other bacteria, thus permitting
ampicillin to act
|
Indications�
Ampicillin
+ Cloxacillin is indicated when broad spectrum coverage involving
these two antibiotics is required:
- Empiric therapy
when the causative organism is unknown
- When Staph. aureus is a likely causative orrganism�- Mixed infections
|
Indications�
-
Respiratory Tract infections
pharyngitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, otitis media, bronchitis, pneumonia
- Skin & Soft Tissue infections�
furunculosis, carbuncle, abscesses, paronychia, pyoderma, traumatic/surgical
wound infection
- Bone & Joint Infections�
osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, surgical infections
|
Dosage
& Administration
Adults
Amp 250+Clox250 capsules / injections 1-2 capsules 3-4 times daily
Children�
15-50 mg of each ingredient/kg body weight/day
|
Tolerability
Possesses the well-known safety of penicillins.�Relatively commoner
adverse effects, if any, include skin rash, G.I. effects such as diarrhoea
and drug hypersensitivity. Safe in children, pregnancy & lactation
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to penicillins
|
Salient
Features of Amp+Clox
- Combination
of 2 time tested, effective and safe penicillins�
- Synergistic combination�
- Broad spectrum coverage of ß-lactamase producing and non ß-lactamase
producing bacteria�
- Pharmacokinetically and chemically compatible combination�
- Oral and parenteral use�
- Suitable for day-to-day infections�
- For empiric therapy and mixed infections�
- ENT/RTI, Skin & Soft Tissue infection, Bone & Joint Infection
|
Advantages
over Fluoroquinolones�
(Ciprofloxacin, Norfloxacin, Sparfloxacin, Pefloxacin)
- Norfloxacin
poorly distributed in the body; chiefly used for GI and urogenital
infections
- Ciprofloxacin mainly effective against gram -ve bacteria; poor efficacy
in staphylococcal and streptococcal infections in day-to-day practice
- Sparfloxacin is needlessly expensive for common infections
- Pefloxacin associated with adverse effects
|
Advantages
over Macrolides�
(Erythromycin, Roxithromycin, Azithromycin)
- Macrolides
are chiefly effective against gram positive organisms, Amp+Clox has
broad spectrum coverage involving gm +ve and gm -ve organisms�
- Even against gm +ve bacteria, cloxacillin is a drug of choice�
- Antibacterial spectrum of macrolides is similar to
each other; pharmacokinetics differ
|
Advantages
over Oral Cephalosporins�
(Cephalexin, Cefadroxil, Cefaclor)
- Oral cephalosporins
are generally not the drugs of first choice for most infections; ampicillin
and cloxacillin have been first line drugs in many infections�
- Oral cephalosporins are costly for day-to-day infections
|
Advantages
over Tetracyclines�
(Tetracycline, Doxycycline)
- Bacterial
resistance is common to tetracyclines�
- Tolerability profile is poorer than penicillins�
- Cannot be administered to children and pregnant women due to adverse
effects on developing bones and teeth
|
Advantages
over SMX-TMP
(Sulfamethoxazole-Trimethoprim)
- Resistance
to sulphonamides is widespread; often only one ingredient is actually
working�
- Optimum tissue concentration ratio of 1:20 is not obtained hence
loss of synergistic activity�
- Sulphonamides are associated with serious adverse effects including
blood dyscrasias
|
|


