|
Inflammation
|
Inflammation
The normal
reaction of living tissue to injury
|
Inflammation
- Cardinal Signs
*
Calor (heat)
* Rubor (redness)
* Tumor (swelling)
* Dolor (pain)
* Functio laesio (loss of function)
|
Causes of Inflammation
1) Mechanical
: trauma (sports injuries, road accidents)�: surgery (post operatively)
2) Physical : heat (burns), cold, radiation, electricity, pressure
3) Chemicals : strong acids, alkalis, drugs
4) Infections : bacteria, viruses, fungi, animal parasites
|
Changes in
Inflammation
*
Vascular changes
- Vasodilation�
- Capillary permeability
* Cellular changes�
- Chemotaxis�
- Diapedesis�
- Phagocytosis
|
Relationship
of Vascular Changes to Cardinal Signs of Inflammation
|
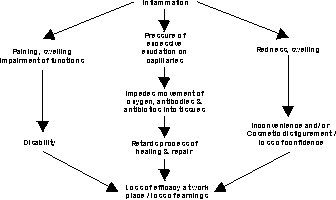
Adverse Consequences
of Inflammation
|
Anti-inflammatory
Drugs
* Steroidal
- Corticosteroids, liberated by adrenal cortex & derivatives eg.,
hydrocortisone, prednisolone, dexamethasone, betamethasone�
* Non-Steroidal
- Non-Steroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) eg., aspirin, ibuprofen,
oxyphenbutazone, piroxicam, diclofenac, mefenamic acid
|
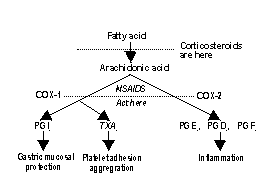
Actions of
Anti-inflammatory Drugs
|
Non-Steroidal
Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDS)
COX-1 & COX-2
inhibitors :
Aspirin, ibuprofen, oxyphenabutazone, piroxicam, diclofenac, mefenamic
acid
Selective COX-2 inhibitors :
Meloxicam, celecoxib, refecoxib
|
NSAIDS - Actions
a)
Anti-inflammatory effect :�Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis
b) Analgesic action :�Increases threshold
for pain perception
c) Antipyretic effect :�Restores the
balance between heat production & heat loss to normal
d) Other effects :�
Antiplatelet effect :- Prevention platelet adhesion & aggregation
useful in prevention MI, stroke
Uricosunic effect :- Urinary excretion of urates useful in
gout
|
|

