|
Antituberculosis
Chemotherapy
|
Older “Standard”
Chemotherapy
(Streptomycin, INH, PAS x 18-24 months)
- Inconveniently
long regimen�
- Poor compliance�
- Low overall success (estimated to be 8% in Indian conditions)
|
In India, it is
estimated that only 30% of cases in the community are diagnosed to
start with, and of this, only 35% remain under treatment for an adequate
period of time. Further, only 75% of these patients who complete the
treatment are finally cured. This means that out of every 100 cases
in the community, the overall level of success is only 8%.
- Fox W., Lung
India, 1984, II, 161-174
|
Newer
Short Course Chemotherapy
- Based on
improving compliance to achieve better overall success
- Drugs must inhibit actively multiplying organisms as well as persisters�
- Main drugs include rifampicin, INH and pyrazinamide, each having
actions against particular populations of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
|
|
|
| |
Cavitary
lesions |
Caseous
lesions |
Macrophages |
| 1.
Location of bacilli |
Extracellular |
Extracellular |
Intracellular |
| 2.
Population of bacilli |
+++ |
++
|
++ |
| 3.
Oxygen tension |
high |
low
|
low
|
| 4.
Medium |
Neutral
/Alkaline |
Neutral
|
Acidic
|
| 5.
Resistant mutants |
Common |
Uncommon |
Uncommon
|
|
|
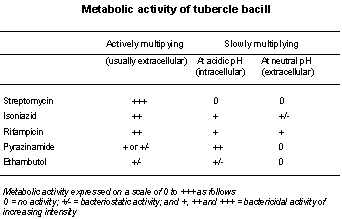
|
Usual Anti
TB Regimen
6
months regimen:
First 2 months
(Intensive phase) : EHRZ�
Next 4 months (Continuation phase) : HR
(H = Isoniazid; R = Rifampicin; Z = Pyrazinamide�
E = Ethambutol)
* Ethambutol
is optional; another drug may be used in its place
* Regimens of longer duration and/or with 3 or 5 drugs in intensive
phase may be used
|
Cardinal
Anti TB drugs- Important features
Rifampicin
-
Active against various mycobacterial populations, hence mainstay of
treatment�
- Very rapid bactericidal action Isoniazid�
- Active against various mycobacterial populations, hence mainstay
of treatment�
- Bactericidal
|
Anti TB drugs
- Important features (contd.)
Pyrazinamide�
- Active against intracellular organisms in acidic pH
- Bactericidal
Ethambutol�
- Bacteriostatic drug, added to regimen to take care of resistance
Other drugs�
- May need to be added to regimen especially in cases of relapse,
because of multi drug resistance (MDR)
|
Daily
Dosages
| |
Adults
|
Children
|
|
Rifampicin
|
400-600
mg
|
10-20
mg/kg
|
|
Isoniazid
|
300
mg
|
5-20
mg/kg
|
|
Pyrazinamide
|
1.5
- 2 g
|
20-35
mg/kg
|
|
Ethambutol
|
15-25
mg/kg
|
15-25
mg/kg
|
|
Some Adverse
Effects of the Main Anti TB drugs
Rifampicin
: brownish discolouration of urine, hepatoxicity Isoniazid : hepatotoxicity,
peripheral neuropathy Pyrazinamide : hepatotoxicity, hyperuricaemia
Ethambutol : optic neuritis
|
Some Other
Anti TB drugs
Capreomycin�
Dosage : 1 g daily (15-20 mg/kg/day) given IM for 60-120 days; then
2-3 times weekly upto 18-24 months
Cycloserine�
Dosage : 250 mg 12 hourly for 2 weeks, increased to 500 mg 12 hourly.
Children 10 mg/kg/day
Ethionamide�
Dosage : 15-20 mg/kg o.d. (max 1 g daily)
Prothionamide�
Dosage :15-20 mg/kg/day (max 1 g daily)
Streptomycin�
Dosage : Adults 0.75-1 g daily. Children 15-20 mg/kg/day. Daily for
1st 2 months; thrice weekly for next 2-6 months
|
|
